The foreskin is a retractable double-layered fold of skin and mucous membrane that covers the glans penis and protects the urinary meatus when the penis is not erect. It is also described as the prepuce, a technically broader term that also includes the clitoral hood in women, to which the foreskin is embryonically homologous.
The outer foreskin is a continuation of the skin on the shaft of the penis, but the inner foreskin is a mucous membrane like the inside of the eyelid or the mouth. The mucocutaneous zone occurs where the outer and inner foreskin meet. Like the eyelid, the foreskin is free to move after it separates from the glans, usually by puberty. Smooth muscle fibres keep it close to the glans but make it highly elastic.
The foreskin is attached to the glans with a frenulum, which helps return the foreskin over the glans. At the end of foreskin, there is a band of tissue called the ridged band, which, according to one study, is rich in nerve endings called Meissner's corpuscles. According to a study by Sorrells et al., the five most sensitive areas of the penis are on the foreskin. The group, Doctors Opposing Circumcision produced a video that provide detailed information.
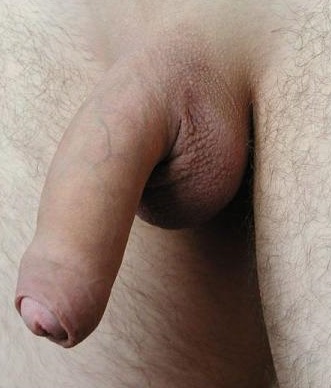
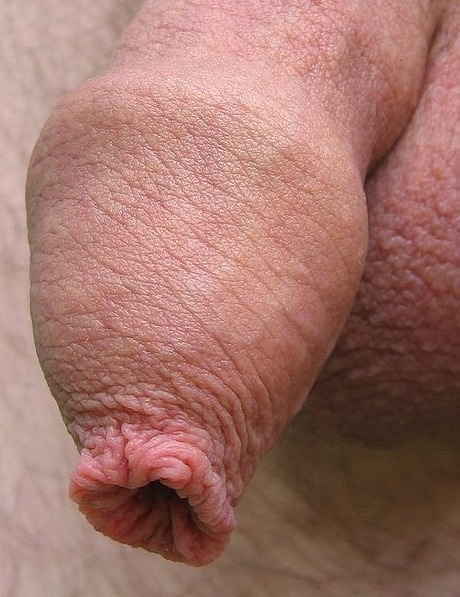
Source: Foreskin, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Source: A Foreskin Retraction Series, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia